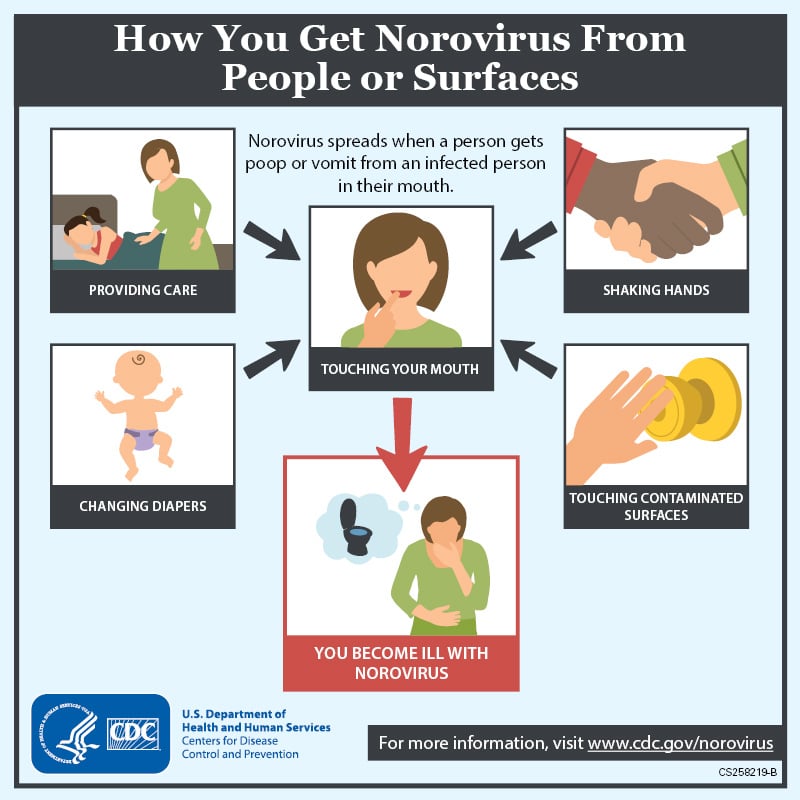
Noroviruses are a group of related viruses that can cause gastroenteritis (GAS-tro-en-ter-I-tis), which is inflammation of the stomach and intestines. This leads to cramping, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Common symptoms include cramping, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Norovirus spreads quickly. It is found in the vomit and stool of infected people. You can get it by eating food or drinking liquids that are contaminated with norovirus, touching surfaces or objects with norovirus on them and then putting your hand or fingers in your mouth. You can also contract Norovirus by having direct contact with a person who is infected, such as caring for someone with norovirus or sharing foods or eating utensils with them.