This page provides information related only to sampling and testing of raw milk that is intended to be marketed as a Grade A pasteurized milk product. For information about raw milk, please visit the Milk Program webpage.
The Milk Bacteriology Laboratory at the Glen F. Baker Public Health Laboratory performs analyses on Grade A raw milk, Grade A pasteurized milk, and various other dairy products to ensure legal compliance with State and Federal standards for interstate shipment. The laboratory works closely with the Environmental Health Branch to ensure the safety and quality of dairy products consumed by the public, and test results are reported to the AR Milk Program for regulatory compliance.
The AR Department of Health is also authorized by state law to certify/approve industry milk laboratories and analysts for drug residue testing. For details about the milk industry laboratory certification/approval process, please contact the state Laboratory Evaluation Officer at 501 661-2738 or [email protected].
Raw & Retail Milk Testing Procedures
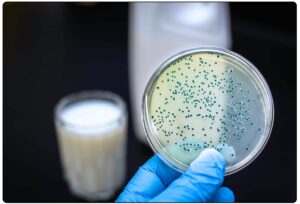
- Aerobic Plate Count: This method is one of the procedures used for the determination of quality and the detection of microbial contamination for raw and retail (processed) milk. For individual producer raw milk, the total bacterial count must not exceed 100,000 per mL. For a retail product, the total count must not exceed 20,000 per mL or gram.
- Detection of Antibiotic/Drug Residues for Raw and Retail Milk: Antibiotic drug therapy is often used during the management of livestock, which runs the risk of drug residue entering the milk supply. Screening for antibiotic residue ensures that milk from treated cows is not sold to the public.
- Somatic Cell Count (SCC): This measurement is an important indicator of milk quality as high counts of SCC can indicate mastitis or abnormal milk secretions in raw milk. Somatic Cell Count for individual producer raw milk must not exceed 750,000 per mL.
- Freezing Point for Raw and Retail Milk: The laboratory uses a Cryoscope to determine the freezing point of a sample, which is used to determine whether water has been added to milk.
- Coliform Test for Retail Milk: This procedure measures the quality of practices used during the processing of dairy products. Coliforms found in pasteurized products can indicate improper pasteurization or contamination after pasteurization. To pass state regulations, retail milk products must not have a coliform count that exceeds 10 per mL or gram.
- Phosphatase for Retail Milk: Thisprocedure is used to determine that retail milk has been pasteurized properly by testing the products for alkaline phosphatase enzyme. The measured enzyme activity must be less than 350 milliunits per liter (mU/L). Food safety organizations such as the FDA and US Center for Disease Control recommend complete pasteurization to kill disease-causing bacteria.
Visit the ADH Milk Program for additional milk safety information and resources.
Contact Us
ADH Office of Environmental Health
Phone: 501-661-2171
Fax: 501-661-2572


