Nutrition in your life
The foods we eat have a huge impact on our health and how long we live. The scientific connection between food and health has been well documented for many decades, with substantial and increasingly robust evidence showing that a healthy lifestyle—including following a healthy dietary pattern— can help people achieve and maintain good health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases throughout all stages of the lifespan: infancy and toddlerhood, childhood and adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy and lactation, and older adulthood.
Reference: Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020-2025
Use MyPlate to make healthier choices
Visit ChooseMyPlate.gov to find practical tools that can help you make healthier food choices.
MyPlate is the federal government’s newest food icon for presenting these guidelines. MiPlato is the Spanish language version. MyPlate and MiPlato highlight the amount of fruit, vegetables, grains, protein foods, and dairy groups needed to make healthy food choices.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Agriculture work together to release the Dietary Guidelines every five years. These guidelines use the newest scientific knowledge to create helpful tips for healthy eating and keeping a healthy weight.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
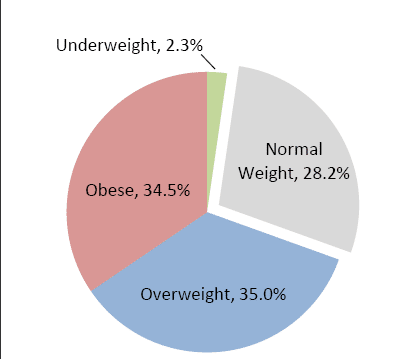
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. It is used to measure overweight and obesity. It is based on a formula of fat to lean body mass.
| Classification | BMI |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 |
| Normal Weight | 18.5 to 24.9 |
| Overweight | 25 to 29.9 |
| Obese | 30.0 and above |
There are some concerns about using BMI as the sole measure of excess weight since it cannot distinguish between fat and muscle. People with a significant amount of muscle may have higher BMIs but not have an unhealthy amount of body fat. In addition, there may be some ethnic or racial differences. For example, those of African and/or Polynesian descent may have less body fat and leaner muscle tissue suggesting higher baseline BMIs for overweight and obesity. Those of Asian and Aboriginal descent, in spite of healthy BMIs, may still be at high risk of weight related problems.
Waist Circumference
In recognition of these potential shortcomings of BMI, another measure of obesity and overweight, waist circumference or stomach fat, is also used.
| Gender | Waist Circumference |
|---|---|
| Men | More Than 40 Inches |
| Women | More Than 35 Inches |


